Gear Pump Displacement Calculator
Calculate the displacement of your gear pump in cubic inches or cubic centimeters per revolution
Displacement Results
Frequently Asked Questions
Gear pump displacement refers to the volume of fluid the pump can deliver per revolution of its drive shaft. It’s a critical parameter that determines the pump’s flow rate when combined with its rotational speed.
If you have access to the gears themselves, use the Gear Dimensions method for greater accuracy. If you only have the pump body, use the Pump Body Dimensions method which provides an approximate calculation.
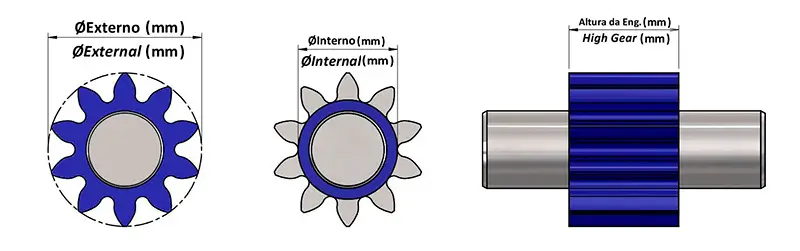
For accurate measurements, disassemble the pump and measure: Outer diameter (D) across gear teeth tips, inner/root diameter (d) across gear teeth bases, and gear width (gW) along the gear’s axis.
Gear pump displacement refers to the volume of fluid a gear pump moves in a single revolution of its gears. It’s a key parameter that determines the pump’s flow rate at a given rotational speed. Essentially, it’s the pump’s capacity to deliver fluid.
Calculation:
Gear pump displacement is typically calculated using the physical dimensions of the gears within the pump. The formula involves factors like gear width, tip diameter, and the distance between gear centers when they are meshed.
Factors Affecting Displacement:
- Gear dimensions:The width and diameter of the gears directly influence the volume enclosed within the gear teeth and thus the pump’s displacement.
- Number of teeth:The number of teeth on the gears can also impact displacement, especially in internal gear pumps.
- Gear material and clearances:The material of the gears and the clearances between the gears and the pump housing can affect the efficiency and thus the effective displacement.
Practical Implications:
- Flow rate:A larger displacement means the pump will deliver more fluid per revolution at a given speed.
- Efficiency:Proper gear dimensions and clearances are crucial for maintaining high pump efficiency, ensuring that the displacement translates to actual flow.
- Application:Displacement is a critical factor in selecting the right gear pump for a specific application, such as hydraulic systems, lubrication, or pumping viscous fluids.
In essence, gear pump displacement is a measure of the pump’s volumetric capacity, which is determined by the geometry of its internal components and affects its performance in various applications.