Sprocket Speed Calculator
Calculate gear ratios, output speeds, and transmission efficiency for chain drive systems
Input Parameters
Number of teeth on the driving sprocket
Number of teeth on the driven sprocket
Rotations per minute of the driving sprocket
Visualization
20 Teeth
40 Teeth
Visual representation of your sprocket configuration
Calculation Results
Output Speed
Speed of the driven sprocket
Gear Ratio
Driven : Drive sprocket ratio
Speed Ratio
Drive : Driven speed ratio
Torque Multiplier
Increase in torque at driven sprocket
Frequently Asked Questions
A sprocket speed calculator helps determine the output speed of a driven sprocket based on the input speed of the drive sprocket and the number of teeth on both sprockets. It’s essential for designing chain drive systems in various mechanical applications.
The formula for calculating sprocket speed is:
Driven Sprocket RPM = (Drive Sprocket Teeth / Driven Sprocket Teeth) × Input RPM
This calculation gives you the rotational speed of the driven sprocket based on the input speed and the gear ratio determined by the number of teeth on each sprocket.
Sprocket size (number of teeth) has an inverse relationship with speed. When the driven sprocket is larger than the drive sprocket, the output speed decreases but torque increases. Conversely, when the driven sprocket is smaller, the output speed increases but torque decreases.
Changing sprocket sizes affects acceleration, top speed, and torque. A larger driven sprocket (or smaller drive sprocket) increases acceleration and torque but reduces top speed. A smaller driven sprocket (or larger drive sprocket) increases top speed but reduces acceleration and torque.
Changing sprocket sizes on a motorcycle or other chain-driven vehicle affects both acceleration and top speed. A larger rear sprocket (or smaller front sprocket) increases acceleration but decreases top speed, while a smaller rear sprocket (or larger front sprocket) increases top speed but decreases acceleration. This is because sprockets alter the final drive ratio, which determines how engine RPM translates to wheel speed.
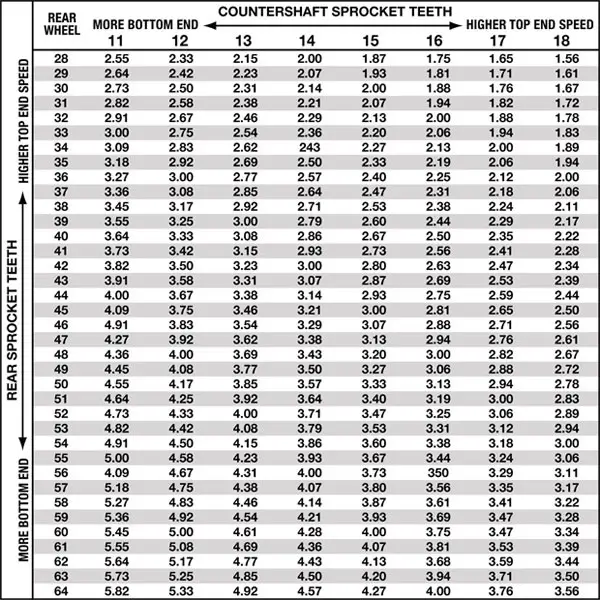
Sprocket Ratio and its Effects:
- Final Drive Ratio:The relationship between the front and rear sprocket sizes is called the final drive ratio. This ratio determines how much engine power is translated into wheel rotation.
- Calculating the Ratio:The sprocket ratio is calculated by dividing the number of teeth on the driven (rear) sprocket by the number of teeth on the driving (front) sprocket.
- Large Rear/Small Front:A larger rear sprocket (or smaller front sprocket) means the rear wheel will rotate more times for each engine revolution, leading to quicker acceleration. However, this also means the engine will reach its maximum RPM at a lower speed, limiting top speed.
- Small Rear/Large Front:Conversely, a smaller rear sprocket (or larger front sprocket) means the rear wheel rotates fewer times for each engine revolution, resulting in a higher top speed. However, this will reduce acceleration and make it feel like the engine is working harder at lower speeds.
In essence:
- Acceleration:A larger rear sprocket (or smaller front sprocket) increases acceleration because it multiplies the engine’s torque at the rear wheel.
- Top Speed:A smaller rear sprocket (or larger front sprocket) increases top speed because it allows the engine to reach a higher gear before hitting its maximum RPM.
Example:
- If a motorcycle has a 16-tooth front sprocket and a 40-tooth rear sprocket, the sprocket ratio is 40/16 = 2.5.
- Changing to a 15-tooth front sprocket would increase the ratio to 40/15 = 2.67, resulting in faster acceleration.
- Changing to a 45-tooth rear sprocket would decrease the ratio to 45/16 = 2.81, also resulting in faster acceleration.
Important Considerations:
- Chain Length:Changing sprocket sizes may require adjusting the chain length to ensure proper tension and fit.
- Riding Style:The best sprocket setup depends on the type of riding you do. For track racing, you might prioritize acceleration and change the sprockets to suit. For long-distance touring, you might prioritize top speed and fuel efficiency.